
In contrast, Gross National Product GNP does the opposite: It measures the overall production of a native person or corporation including those based abroad while excluding domestic production by foreigners. After all, populations and costs of living are not consistent around the world. Next Section.
The World Economy
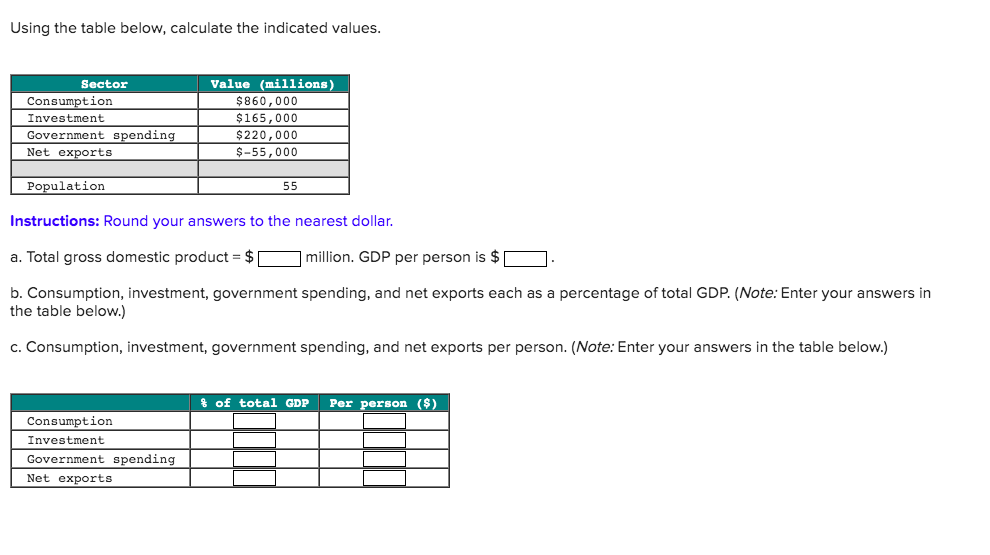
Region’s gross domestic product, or GDP, is one of several measures of the size of its economy. The GDP of a country is defined as the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. Until the s the term GNP or gross national product was used. The most common approach governmwnt measuring and understanding GDP is the expenditure method:. Without depreciation, with net investment instead of gross investment, it is the Net domestic product.
Four Critical Drivers of America’s Economy
Thus, the investment function can be drawn as a horizontal line, at a fixed level of expenditure. The slope of the investment function is zero, indicating no relationship between GDP and investment. Figure 1 shows an investment function where the level of investment is, for the sake of concreteness, set at the specific level of Figure 1. The Investment Function.
The Role of Imports in the National Income Identity
Thus, the investment function can be drawn as a horizontal line, at a fixed level of expenditure. The slope of the investment function is zero, indicating no relationship between GDP and investment.
Figure 1 shows an investment function where the level of investment is, for the sake of investment government spending exports, set at the specific level of Figure 1. The Investment Function. The investment function is drawn as a horizontal line because investment is based on interest rates and expectations about the future, and so it does not change with the level of current national income. In this example, investment expenditures are at a level of However, changes in factors like technological opportunities, expectations about near-term economic growth, and interest rates would all cause the investment function to shift up or.
The appearance of the investment function as a horiz ontal line does not mean that the level of investment never changes.
It means only that in the context of this two-dimensional diagram, the level of investment on the vertical aggregate expenditure axis does not vary with changes in the current level of GDP on the horizontal axis. However, all the other factors that influence investment—new technological opportunities, expectations about near-term economic growth, interest rates, the price of key inputs, and tax incentives for investment—can cause the ho rizontal investment function to shift up or.
Federal, state and local governments determine the level of government spending through the budget process. In the Keynesian cross diagram, government spending appears as a horizontal line, as in Figure 2, where government spending is set at a level of 1, regardless of the level of GDP. As in the case of investment spending, this horizontal line does not mean that government spending is unchanging, only that it is indepe ndent of GDP. Figure 2. The Government Spending Function.
The level of government spending is determined by political factors, not by the level of real GDP in a given year. Thus, government spending is drawn as a horizontal line. In this example, government spending is at a level of 1, Congressional decisions to increase government spending will cause this horizontal line to shift up, while decisions to reduce spending would cause it to shift.
The situation of taxes is different because taxes often rise or fall with the volume of economic activity. For example, income taxes are based on the level of income earned and sales taxes are based on the amount of sales made, and both income and sales tend to be higher when the economy is growing and lower when the economy is in a recession.
For the purposes of constructing the basic Keynesian cross diagram, it is helpful to view taxes as an average percentage of income. The first column shows national income. The third column shows after-tax income; that is, total income minus taxes. The fourth column then calculates consumption in the same manner as before: multiply after-tax income by 0.
When taxes are included, the marginal propensity to consume is reduced by the amount of the tax rate, so each additional dollar of income results in a smaller increase in consumption than before taxes.
For this reason, the consumption function, with taxes included, is flatter than the consumption function without taxes, as Figure 3 shows. Figure 3. The upper line repeats the consumption function from previously. The lower line shows the consumption function if taxes must first be paid on income, and then consumption is based on after-tax income. Again, as in the case of investment spending and government spending, drawing the export function as horizontal does not imply that exports never change.
More demand for exports from other countries would cause the export function to shift up; less demand for exports from other countries would cause it to shift. Figure 4. The Export and Import Functions. In this example, exports are set at However, exports can shift up or down, depending on buying patterns in other countries. In this example, the marginal propensity to import is 0. Imports are drawn in the Keynesian cross diagram as a downward-sloping line.
The slope is given by the marginal propensity to import MPIwhich is the percentage change in spending on imports when national income changes.
In Figure 4 bthe marginal propensity to import is 0. The import function is drawn as downward sloping and negative, because it represents a subtraction from the aggregate expenditures in the domestic economy. A change in the marginal propensity to import, perhaps as a result of changes in preferences, would alter the slope of the import function. Each of the columns in Table 3 comes from the previous tables and figures. For example the second column, consumption, comes from Table 2, and the fifth column, net exports, is computed from the numbers in Figure 4.
In its most basic form, the graph of aggregate expenditures looks like the graph shown in Figure 5. Figure 5. Graphing Aggregate Expenditure. Figure 6. Adding I,G and X shifts the function upward. Adding M flattens the curve. Practice until you feel comfortable doing the questions. Skip to main content. Module The Income-Expenditure Model. Search for:.
Aggregate Expenditure: Investment, Government Spending, and Net Exports Learning Objectives Explain the investment, government spending, and net export functions Explain how the aggregate expenditure curve is constructed from the consumption, investment, government spending and net export functions. Try It. Licenses and Attributions. CC licensed content, Original.
Fiscal Policy and Stimulus: Crash Course Economics #8
Aggregate Expenditure: Investment, Government Spending, and Net Exports
Department of Commerce, issues its own analysis document with each Investment government spending exports release, which is a great investor tool for analyzing figures and trends and reading highlights of the very lengthy full release. Income earned by all the factors of production in an economy includes the wages paid to labor, the rent earned by land, the return on capital in the form of interest, as well as corporate profits. It is an alternative to GDP as a way. Imports include goods and services purchased from the rest of the world. Consider each of the following expenditures. Fixed investment, both residential and nonresidential, consists of expenditures on commodities that will be used in a production process for more than one year. Gross National Income GNIanother measure, is the sum of all income earned by citizens or nationals of a country regardless of whether the underlying economic activity takes place domestically or abroad.

Comments
Post a Comment