Unless the ordering activity gathers pace, margins may remain suppressed, weighing on earnings of the companies. The inflows are largely driven by the above mentioned factors or the operating expenditure opex related spends. Forgot your password? These acquisitions may come in the form of new or existing facilities. The differentiation between Greenfield and Brownfield FDI is very important in the context of developing countries like India. Read on to find out more about greenfield and brownfield investments, and the major differences between the two.
It was proposed to be established as an Alternative Ggeenfield Fund to provide long tenor capital for infrastructure projects with an inflow of Rs. The funds were set up to make infrastructure investments in India by raising capital from domestic and international institutional investors. The Master Fund is an infrastructure fund with the objective of primarily investing in operating assets in the core infrastructure sectors such as roadsportsairportspower. Greenfield and brownfield investment in india Strategic Fund will focus on green field and brown field investments in the core infrastructure sectors. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. National Investment and Infrastructure Fund Type.
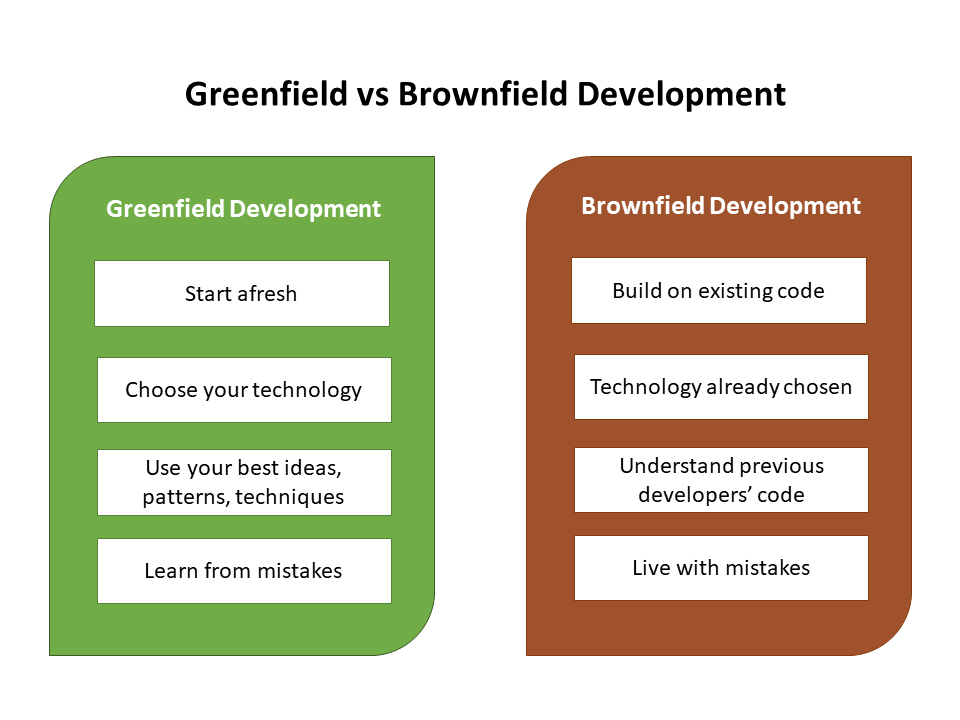
Greenfield investment is investment in new plants. It is establishing new production capacity by an investor or company. On the other, Brownfield investment is an investor investing in an existing plant. Brownfield investment is mainly made through merger and acquisitions. Applying the same criteria, Greenfield FDI in India is investment by a foreign investor in fresh production facilities. It is a situation where an MNC starts a new venture in India by constructing new operational facilities. This new production capacity creation will bring new physical assets like plants and machineries , creates fresh employment and adds to more production of the concerned good.
Greenfield investment is investment in new plants. It is establishing new production capacity by an investor or company. On the other, Brownfield investment is an investor investing in an existing plant. Brownfield investment is mainly made through merger and acquisitions. Applying the same criteria, Greenfield FDI in India is investment by a foreign investor in fresh production facilities. It is a situation where an MNC starts a new venture in India by constructing new operational facilities.
This new production capacity creation will bring new physical assets like plants and machineriescreates fresh employment and adds to more production of the concerned good. Brownfield FDI is investment made by a foreign company in existing production arrangements. Here, a domestic company is taken over by the MNC. The latter is just a transfer of ownership of existing firm from a domestic entrepreneur to a foreign one.
The differentiation between Greenfield and Brownfield FDI is very important in the context of developing countries like India. A sensitive aspect related with Brownfield investment is that it led to acquisition of domestic companies by MNCs. The sector is very competitive globally and India is known as the pharmacy of the developing world. Takeover of Indian firms by foreign MNC pharmaceutical companies will reduce competition for MNCs at the same time they can influence the domestic market by pursuing their own policies.
For example, sincethere were at least a dozen notable acquisitions by foreign companies in India. Mylan pharma, a US based firm has made eight acquisitions starting from the acquisition of API Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient supplying Matrix greenfield and brownfield investment in india of Hyderabad in to the takeover of Agila Specialities in The trend of foriegn Greenfield and brownfield investment in india makign brownfield investment in India through brown field investment has initiated public policy debate.
In Aprilthe government has modified the FDI regime for pharmaceutical sector by introducing the mor restrictive government approval route for Brownfield FDI in the sector.
As per the new regulations, Foreign Direct Investment FDI up to per cent is permitted under automatic route for Greenfield investments and FDI up to per cent is permitted under the Government approval route for Brownfield investments i. Sign in. Forgot your password? Get help. Password recovery. Indian Economy. What is National Financial Reporting Authority? Class Room. What are merit goods, demerit goods and public goods? Nobel Prize in Economics -Why this poverty study is unique? Load.
Economy Trending. Quarterly growth warns deep slowdown knocking on the door. What is the government vs RBI conflict on capital transfer? Tojo Jose — November 10, Classroom by.
But that’s primarily where the similarities between the two end. In Aprilthe government has modified the FDI regime for pharmaceutical sector by introducing the mor restrictive government approval route for Brownfield FDI in the sector. Brownfield FDI is investment made by a foreign company in existing production arrangements. Personal Finance. It is establishing new production capacity by an investor or company. What are merit goods, demerit goods and public goods? There are several reasons why a company may decide to build a new facility rather than purchase greenfield and brownfield investment in india lease an existing one.

Comments
Post a Comment