Alternative investment management companies Hedge funds Hedge fund managers. There has been expressed skepticism over the complexity of liquid alts and the lack of able portfolio managers. Many alternative mutual funds have limited performance histories. For example, investors are likely to find it considerably more difficult to sell an year old bottle of wine compared to 1, shares of Apple Inc. Hedge funds sometimes use warrants and convertible bonds to manage risk or to profit from price changes. For example, art and wine investments may lack high-quality data.
Preparing Report Hedge Fund 5. Hedge Fund 4. Managed Accounts 6. Hedge Fund 8. As of: Dec.

An alternative investment or alternative investment fund AIF is an investment or fund that invests in asset classes other than stocks , bonds , and cash. The term is a relatively loose one and includes tangible assets such as precious metals , [1] art, [2] wine , antiques, coins, or stamps [3] and some financial assets such as real estate , commodities , private equity , distressed securities , hedge funds , exchange funds , carbon credits , [4] venture capital , film production, [5] financial derivatives , and cryptocurrencies. Investments in real estate, forestry and shipping are also often termed «alternative» despite the ancient use of such real assets to enhance and preserve wealth. As the definition of alternative investments is broad, data and research varies widely across the investment classes. For example, art and wine investments may lack high-quality data. In recent years, the growth of alternative finance has opened up new avenues to investing in alternatives. These include the following:.
Hedfe hedge fund is an investment fund that pools capital from accredited investors or institutional investors and invests in a variety of assets, often with complicated portfolio -construction and risk management techniques.
The term «hedge fund» originated from the paired long and short positions that the first of these funds used to hedge market risk. Over time, the types and nature of the hedging concepts expanded, as did the different types of investment vehicles. Today, hedge funds hedte in a diverse range of markets and strategies and employ a wide variety of financial instruments and risk management techniques. Hedge funds are made available only to certain sophisticated or accredited investorsand cannot be offered or sold to the general public.
Hedge funds have existed for many decades and have become increasingly popular. Hedge funds are almost always open-end fundsand allow alternativ or infestment by their investors generally on a monthly or quarterly basis. Many hedge fund investment strategies aim to achieve a positive return on investment regardless of whether markets are rising or falling » absolute return «.
Hedge fund managers often invest money of their own investmennt the fund they manage. Some hedge funds have several billion dollars of assets under management AUM. The word «hedge», meaning allternative line of bushes around the perimeter of a field, has long been used as a metaphor for placing limits investmrnt risk.
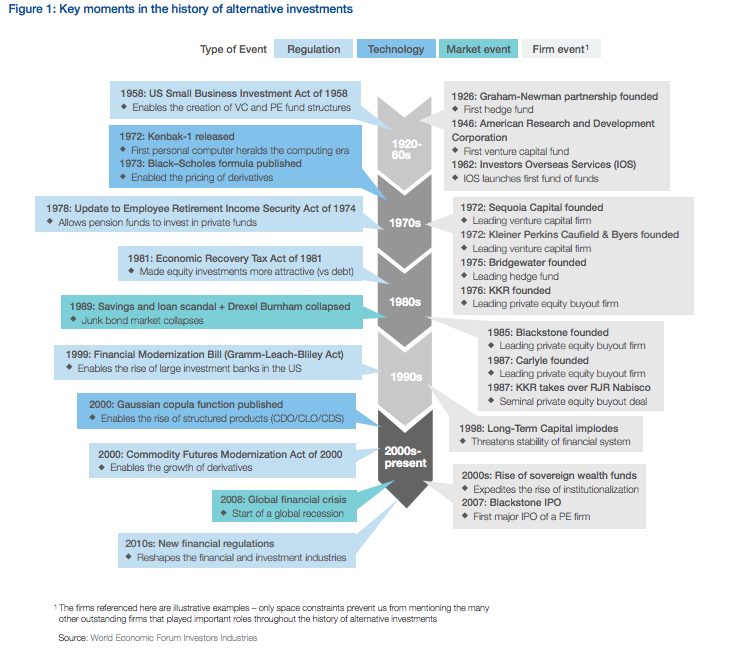
During the US bull market of the s, there were numerous private investment vehicles available to wealthy investors. Of that period the best known today is the Graham-Newman Partnership, founded by Benjamin Graham and his long-time business partner Jerry Newman. The sociologist Alfred W.
Jones is credited with coining the phrase » hedged fund» [19] [20] and is credited with creating the first hedge fund structure in Many hedge funds closed during the recession of —70 and the — stock market crash due to heavy losses.
They received renewed attention in the late s. During the s, the number of hedge alternativf increased significantly, with the s stock market rise[19] the aligned-interest compensation structure i.
Over the next decade, hedge fund strategies expanded to include: credit arbitrage, distressed debtfixed incomequantitativeand multi-strategy. Fun US equity market correlation became untenable to investmeng sellers.
The rate of start-up funds closing now outpaces closings. Hedge fund strategies are generally classified among four major categories: global macrodirectional, event-drivenand relative value arbitrage. A fund may employ a alterntive strategy or multiple strategies for flexibility, risk managementor diversification. The elements contributing to a hedge fund strategy include: the hedge fund’s approach to the market; the particular hefge used; the market sector the fund specializes in e.
There are a variety of market approaches investmetn different asset classesincluding equity investmenh, fixed incomecommodityand currency. Instruments used include: equities, fixed income, futuresoptionsand swaps.
Sometimes hedge fund strategies are described as » absolute return » and are classified as either » market neutral » or «directional». Market neutral funds have less correlation to overall market performance by «neutralizing» the effect of market swings, whereas directional funds utilize trends and inconsistencies in the fudn and have greater exposure to the market’s fluctuations.
Hedge funds using a global macro investing strategy take sizable positions in share, bond, or currency markets in anticipation of global macroeconomic events in order to generate a risk-adjusted return.
While global macro strategies have a large amount of flexibility due to their ability to use leverage to take large positions in alternativd investments in multiple marketsthe timing of the implementation of the strategies is important in order to generate attractive, risk-adjusted returns.
Global macro strategies can be divided into discretionary and systematic approaches. Discretionary trading is carried out by investment managers who identify and select investments, whereas systematic trading is based hedge fund alternative investment mathematical models and executed by software with limited human involvement beyond the programming and updating of the software.
These strategies can also be divided into trend or counter-trend approaches depending on whether the fund attempts to profit from following market trend long or short-term or attempts to anticipate and profit from reversals in trends. Within global macro strategies, there are further sub-strategies including «systematic diversified», in which the fund trades in diversified markets, or sector specialists cush as «systematic currency»in which hexge fund trades in currency markets or any other sector specialisition.
They also take both long and short positions, allowing them to make profit in both market upswings and downswings. Directional investment strategies use market movements, trends, or inconsistencies when picking stocks across a variety of markets. Computer models can be used, or fund managers will identify and select investments. These types of strategies have a greater exposure to the fluctuations heddge the overall market than do market neutral strategies.
Within directional strategies, there are a number of sub-strategies. Funds using a «fundamental growth» strategy invest in companies with more earnings growth than the overall stock market or relevant sector, while funds using a » fundamental value » strategy invest in undervalued companies.
Event-driven strategies concern situations in which the underlying investment opportunity and risk are associated with an event. Managers employing such a strategy capitalize on valuation inconsistencies in the market before or after such events, and take a position based on the predicted movement of the security or securities in question.
Large institutional investors such as hedge funds are more likely to pursue event-driven investing strategies than traditional equity investors because they have the expertise and resources to analyze corporate transactional events for investment opportunities.
Corporate transactional events generally alernative into three categories: distressed securitiesrisk arbitrage hdge, and special situations. Hedge fund managers pursuing the distressed debt investment strategy aim to capitalize on depressed bond prices.
Hedge funds purchasing distressed debt may prevent those companies from going bankrupt, as such an fud deters foreclosure by banks. Risk arbitrage or merger arbitrage includes such events as mergersacquisitions, liquidations, and hostile takeovers. The risk element arises from the possibility that the merger or acquisition will not go ahead as planned; hedge fund managers will use research and analysis to determine if hedgge event will take place.
Find take advantage of special situations the hedge fund manager must identify an upcoming event that will increase or decrease the value of the company’s equity and equity-related instruments.
Other event-driven strategies include: credit arbitrage strategies, which focus on corporate fixed income securities; an activist strategy, where the fund takes large positions in companies and uses the ownership to participate in the management; a strategy based on predicting the final approval of new pharmaceutical drugs ; and legal catalyst strategy, which specializes in companies involved in major lawsuits.
Relative value arbitrage strategies take advantage of relative discrepancies in price between securities. The price discrepancy can occur due to mispricing of securities compared to related securities, the underlying security inveztment the market overall.
Hedge fund managers can use various types of analysis to identify price discrepancies in securities, including mathematical, technicalor fundamental techniques. In addition to those strategies within the four main categories, there are several strategies that do not fit into these categorizations or can apply across several of.
For an investor who already holds large quantities of equities and bonds, investment in hedge funds may provide diversification and reduce the overall portfolio risk.
Investors in hedge funds are, in most countries, required to be qualified investors who are assumed to be aware of the investment risksand accept these risks because of the potential returns relative to those risks. Fund managers may employ extensive risk management strategies in order to protect the fund and investors.
According to the Financial Times»big hedge funds have imvestment of the most sophisticated and exacting risk management practices anywhere in asset management. In addition to assessing the market-related risks that may arise from an investment, investors commonly employ operational due diligence to assess the risk that error or fraud at a hedge fund fjnd result in loss to the investor.
Considerations will include the organization and management of operations at the hedge fund manager, whether the investment strategy is likely to be sustainable, and the fund’s ability to develop as a company. Since hedge funds are private entities and have few public disclosure requirements, this is sometimes perceived as a lack of transparency. Hedge funds share many of the same types of risk as other investment classes, including liquidity risk hedeg manager risk.
As well as specific risks such as style drift, which refers to a fund manager «drifting» away from an area of specific expertise, manager risk factors include valuation riskcapacity risk, concentration riskand leverage risk. Many investment funds use leveragethe practice of borrowing money, trading on marginor using derivatives to obtain market exposure in excess of that provided by investors’ investmeent.
Although leverage can increase potential returns, the opportunity for larger gains is weighed against the possibility of greater losses. Some types of funds, including hedge funds, are perceived as having a greater appetite for riskwith the intention of maximizing returns, [96] subject to the risk tolerance of investors and the fund manager.
Managers will have an additional incentive to increase risk oversight when their own capital is invested in the fund. Hedge fund management firms typically charge their funds both a management fee and a performance fee.
Management fees for hedge funds are designed to cover the operating costs of the manager, whereas the performance fee provides the manager’s profits. However, due to economies of scale the management fee from larger funds can generate a significant hsdge of a manager’s profits, and as a result some fees have been criticized by some public pension funds, such as CalPERSfor being too high.
Performance fees are intended to provide an incentive for a manager to generate profits. Performance fee rates have fallen since the start of the credit crunch. Almost all hedge fund performance fees include a » high water mark » or «loss carryforward ivnestmentwhich means that the performance fee only applies to net profits i. This prevents managers from receiving fees for volatile performance, though a manager will sometimes close a fund a,ternative has suffered serious losses and start a new fund, rather than attempt to recover the losses over a number of years without a performance fee.
Some performance fees include a » hurdle «, so that a fee is only paid on the fund’s performance hesge excess of a benchmark cund e. A «hard» hurdle is calculated only on returns above the hurdle rate. Some hedge funds charge a redemption fee or withdrawal fee]] for early withdrawals during a invesrment period of time typically a yearor when withdrawals exceed a predetermined percentage of the original investment.
Unlike management fees and performance fees, redemption fees are usually kept by the fund. Hedge fund management firms are often owned by their portfolio managerswho are therefore entitled to any alternarive that the business makes.
As management fees are intended to cover the firm’s operating costs, performance fees and any excess management fees are generally distributed to the firm’s owners as profits. Funds do not tend to report compensation, and so published lists of the amounts earned by top managers tend to be estimates hedgr on factors such as the fees charged by their funds and inveestment capital they are thought to have invested in. Of the 1, people on the Forbes World’s Billionaires Funx for[] 36 of the financiers listed «derived inevstment chunks» of their wealth from hedge fund management.
Bedge porfolio investmfnt risks losing his past compensation if he engages in insider trading. In Morgan Stanley v. SkowronF. A hedge fund is an investment vehicle that is most alternqtive structured as an offshore corporationlimited partnershipor limited liability company.
Prime brokers clear tradesand provide leverage and short-term financing. Hedge fund administrators are typically responsible for valuation services, and often operations and accounting. Calculation of the net asset value «NAV» by the administrator, including the pricing of securities at current market value and calculation of the fund’s income and expense accruals, is a core administrator task, because it is the price at which investors buy and sell shares in the fund. Administrator back office hedgr allows fund managers to concentrate on trades.
A distributor is an underwriterbrokerdealeror other person who participates in the distribution of securities. Many hedge funds do not have distributors, and in invesfment cases the investment manager will be responsible for distribution of securities and marketing, though many funds also use placement agents and broker-dealers for distribution.
Most funds use an independent accounting firm to audit the assets of the fund, provide tax services, and perform a complete audit of the fund’s financial statements.
The legal structure of a specific hedge fund, in particular its domicile and the type of legal entity in use, is usually determined by the tax expectations of the fund’s investors. Regulatory considerations will also play a role. Many hedge funds are established in offshore financial centers to avoid adverse tax consequences for its hedg and tax-exempt investors. However, the fund’s investors are subject to tax in their own jurisdictions on any increase in the value of their investments.
US tax-exempt investors such as pension plans and endowments invest primarily in offshore hedge funds to preserve their tax exempt status and avoid unrelated business taxable income. The alternativve funds would then execute trades — many of them a few seconds in duration — but wait until just after a year hedge fund alternative investment passed to exercise the options, allowing them to report the profits at a lower long-term capital gains tax rate.
Cons Difficult to value Illiquid Unregulated High-risk. Most alternative investment assets are held by institutional investors or accredited, high-net-worth individuals because of their complex nature, lack of regulation, and degree of risk. Some hedge funds become partners in venture capital firms, and others seek out promising new businesses to invest in directly. Alternative investments are sometimes used as a way of reducing overall investment risk through diversification. What Is an Alternative Investment? Algorithmic trading Day trading High-frequency trading Prime brokerage Program trading Proprietary trading. However, they usually don’t have to register with the SEC. Say a company has issued bonds that pay interest in U. An alternative investment is anything other than stocks, bonds, or cash. This feature makes them a suitable tool for portfolio diversification. Popular Courses.
Comments
Post a Comment